Blockchain and distributed ledger technology (DLT)
Blockchain falls under the umbrella of Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT), a broader concept encompassing various decentralized data management systems. Blockchain, however, stands out as a specific type of DLT, primarily designed for handling digital currency transactions.
Blockchain and distributed ledger technology (DLT) are frequently used interchangeably, but they have several important distinctions. Blockchain is a distinct form of Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) distinguished by its sequential blocks that store transaction information and are safeguarded using cryptographic methods. DLT is a comprehensive term that includes different distributed ledger systems, such as blockchain.
An Investigation of Distributed Ledger and Related Terms: Key Terminologies
As we further explore the exciting area of distributed ledgers, we will undoubtedly come across other related technologies and terms. Let’s go on a journey to learn some important terms that can help you navigate this ever-evolving landscape:
Distributed ledger technology (DLT)
A distributed ledger is a database that is shared and synchronized across multiple participants in a network. This means that each participant has a copy of the database, which they can use to verify transactions and ensure that no one can tamper with the data.
Categories of distributed ledger
Permissioned
In this, nodes must first obtain authorization from a central authority before they can access or update the network. This authorization process typically involves identity verification to ensure that only authorized participants can join the network.
Permissionless
There is no central authority to validate transactions. Instead, the nodes in the network collectively validate transactions using a consensus mechanism.
Hybrid
Hybrid DLTs incorporate elements of both permissionless and permissioned DLTs, aiming to leverage the strengths of each while mitigating their respective weaknesses.
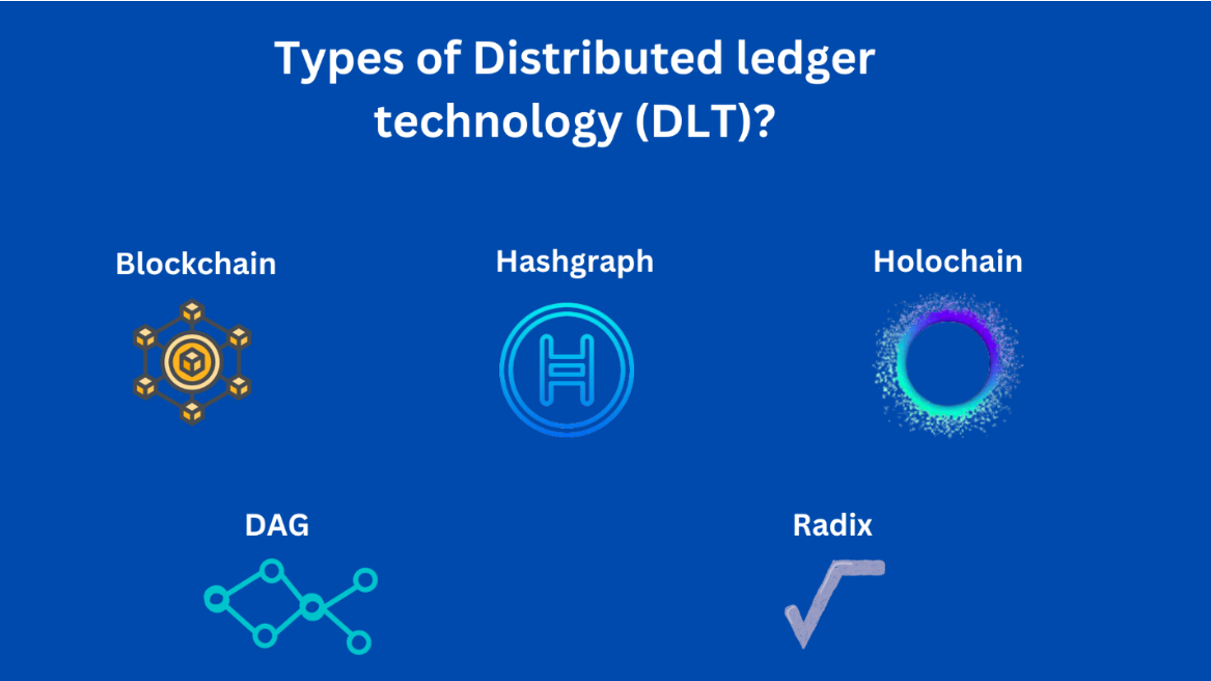
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) encompasses a diverse range of technologies, each with unique characteristics and applications. While they share the common trait of a decentralized database, they differ in their underlying data structures, consensus mechanisms, transparency levels, and immutability features.
● Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology (DLT) that stores data in blocks linked together in a chain. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. This structure makes it extremely difficult to tamper with the data, as any change to a block would also change the hashes of all subsequent blocks.
● Hashgraph uses a unique consensus mechanism called virtual voting to achieve consensus among network participants. This mechanism allows for faster and more efficient transaction processing compared to other DLTs, such as blockchain.
● Holochain introduces a unique concept where each node maintains its own chain of blocks. This decentralized architecture eliminates the need for global consensus mechanisms, enhancing scalability and data integrity.
● Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) utilize a distinct data structure to organize transactions, these transactions are linked together in a directed graph structure, where each transaction references two previous transactions. This structure allows for parallel processing of transactions, significantly enhancing throughput.
● Radix employs a unique sharding approach combined with a novel consensus mechanism to achieve high transaction throughput and low latency.
What is Blockchain?
As we discussed above, blockchain is the basic type of DLT, consisting of a chain of connected blocks, each containing data and a unique code called a “hash” that links it to the previous block. It’s called a “blockchain” because it’s made up of a chain of these blocks, making it a reliable and tamper-resistant way to record and manage information. This technology is used for various purposes, including tracking cryptocurrency transactions, verifying ownership of digital items, and ensuring the security and transparency of data.
Want to learn more about blockchain ( share blockchain link here)
Features of blockchain and DLT
Decentralization is a key characteristic of distributed ledger technologies (DLTs) like blockchain and offers several advantages over centralized systems. In a centralized network, a single point of failure, such as a malfunctioning central server or a malicious attack, can disrupt the entire network. This vulnerability can lead to downtime, data loss, and financial losses.
Transparency is a hallmark of distributed ledger technologies (DLTs) like blockchain. This transparency stems from the inherent nature of DLTs, where all transactions are recorded on a shared, immutable ledger that is accessible to all participants in the network. This public accessibility ensures that everyone can view and verify the transaction history, fostering trust and accountability among network members.
Scalability, distributed ledger technologies (DLTs) are inherently scalable due to their decentralized architecture and the availability of various consensus mechanisms. DLTs in blockchain can distribute the workload across multiple nodes in the network. This distribution allows the system to handle a larger volume of transactions without compromising performance or efficiency.
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement embedded in lines of code in blockchain. They operate on the DLT, leveraging its decentralized, immutable, and transparent nature to automate the execution of agreements without the need for intermediaries.
So ! Blockchain and distributed ledger technology (DLT) are related but distinct concepts. Reason is that Blockchain is a specific type of Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT). DLT is the broader category encompassing various technologies for recording and sharing data in a decentralized way. Blockchain, with its sequential chain of blocks, is just one implementation of DLT, and there are other DLT variations like Hashgraph, Holochain, and more, each with its own unique approach to achieving decentralized consensus and data management.