What are the top features of Blockchain?
At times, we wonder why we use blockchain, what features it should have, and what it can achieve for the digital world? The numerous features of the blockchain are discussed below in efficient manner.
- Decentralized
Blockchain doesn’t depend on a single central authority. Instead, it operates through a decentralized network of computers called nodes. This decentralization enhances security and transparency that reduces the risk of a single point of failure. While some blockchains, especially private ones, might allow a limited group more control, the basic idea of decentralization remains a key feature in Public (Permissionless) blockchains like Ethereum and Bitcoin.

- Transparency:
Every transaction on a blockchain is recorded in a distributed ledger that is open to anyone. This transparency has the potential to combat corruption and ensure accountability. However, it’s crucial to acknowledge that while transparency can be a valuable tool in reducing fraud and ensuring responsibility, it also raises issues about privacy.

- Immutability
Once data is recorded, it’s nearly impossible to change. Each block’s cryptographic link to the prior one forms an unbroken chain. Modifying one block necessitates changing all following blocks with network consensus, making unauthorized alterations highly unlikely, bolstering security and trust in the system.
- Security
Blockchain uses cryptographic techniques to secure data and control access. Each block in the chain is linked to the previous one, creating a secure, tamper-proof system. This makes it very difficult for malicious actors to manipulate the data.

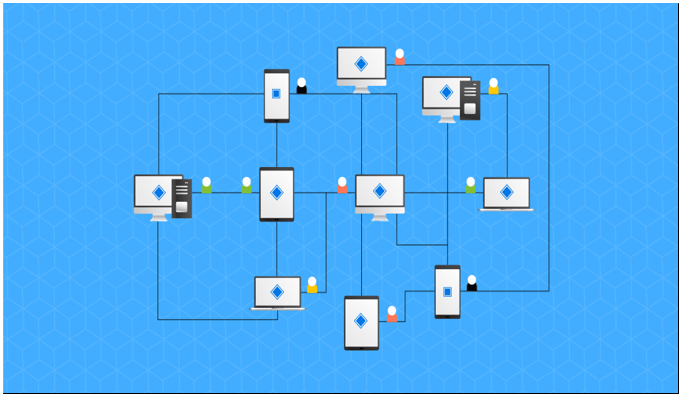
- Consensus Mechanisms
These mechanisms are responsible for ensuring that all participants in a blockchain network agree on the state of the ledger and the validity of transactions. Common consensus mechanisms include Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS), which help validate and add new transactions to the blockchain. These mechanisms enhance security and maintain the integrity of the blockchain for making it a reliable and trustable system.
- Smart Contracts
A blockchain are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automatically enforce and facilitate the execution of contractual agreemen ts when specific conditions are met.

- Speed and Efficiency
An essential feature of some blockchain networks, Blockchain can facilitate faster and more efficient transaction processing, especially for cross-border payments. These improvements are due to the use of consensus mechanisms that reduce settlement time.

What are the Use Cases of blockchain?
Blockchain’s versatility and its capacity to offer secure, transparent, and immutable transaction solutions make it a technology with broad and continually expanding applications across various sectors. Let’s explore the primary use cases of blockchain technology:
- Cryptocurrency
It represents decentralized digital currencies (such as Bitcoin) that leverage blockchain for secure and borderless transactions, reshaping traditional finance systems.
- Healthcare
Blockchain safeguards patient data through encryption and immutability, simplifying clinical trials and ensuring drug traceability. It enhances telemedicine, streamlines insurance claims with smart contracts. Blockchain empowers patients, lowers costs, and transforms healthcare into an efficient, patient-centered, and secure ecosystem.
- Finance and banking
This technology is considered as a game-changer in finance and banking. It ensures secure, transparent, and efficient transactions by eliminating the need for intermediaries. It streamlines cross-border transfers and automates operations through smart contracts that boosting transparency, minimizing fraud, and fostering trust in financial systems.
- Real estate
It modernizes real estate with transparent, tamper-proof property records. Blockchain simplifies transactions, reduces fraud, and bolsters trust in land registries.
- Supply chain and logistics
Blockchain records every step of a product’s journey, from production to delivery, enhancing trust and reducing fraud. This technology streamlines logistics, reduces inefficiencies, and ensures the authenticity and quality of goods.
- Voting system
It ensures that votes are encrypted, tamper-proof, and easily auditable. Blockchain simplifies the process to reduces fraud, and increases trust in election outcomes.In short, blockchain technology offers a versatile array of solutions across various sectors. From revolutionizing finance and healthcare to securing real estate and enhancing supply chain management, blockchain’s ability to provide transparency, security, and efficiency is reshaping industries and fostering trust. Moreover, its role in voting systems ensures the integrity of democratic processes.