WHAT IS COMPUTER VISION?
Computer vision is a field of artificial intelligence that uses machine learning and neural networks to train systems and machines how to understand digital photos, videos, along with other visual inputs, and provide suggestions or take responses when faults or errors are detected.
Throughout the last two decades, novel methods such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and computer vision have moved from study and development to industrial and popular applications. These innovations allowed for autonomous robot manufacturing, vehicle assistance structures, and remote visualization of images, making computer vision and machine learning technologies more appealing and enticing tech sector corporations and start-ups to reap the rewards.
Computer vision is a multidisciplinary domain that seeks to equip computer systems with human-like visual perception skills. It helps computers to process, analyze, and properly comprehend our visual environment, allowing them to extract meaningful information from photos and video data in the same manner that humans do. Modern computer vision employs machine learning, a subset of artificial intelligence, by training machines to learn for themselves as time passes. Machine learning algorithms use prior experiences and judgements to generate suitable reactions with little or no human interaction. This allows computers to grasp and evaluate complicated digital systems better than humans.
How does computer vision work?
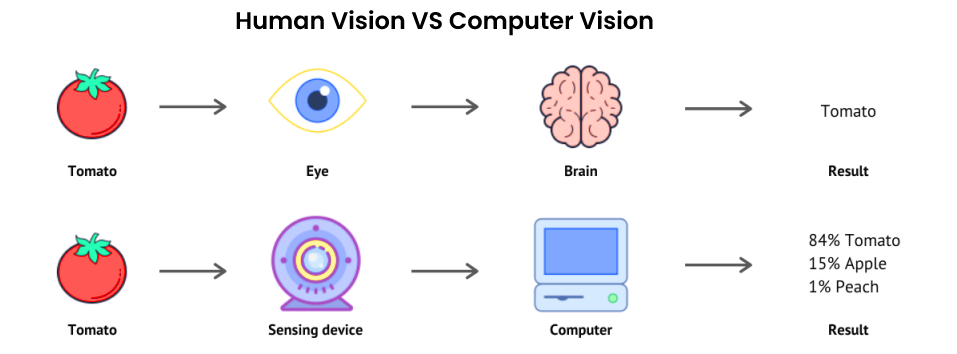
Computer vision is the recognition of pictures using machine learning and convolutional neural networks (CNN). Deep learning employs computational models to instruct a computer about the setting of visual input, allowing it to “look” at and discriminate between pictures. A CNN divides pictures into pixels using tags/labels, performs convolutions, and makes recommendations based on what it observes. The neural network performs convolutions and tests the accuracy of its forecasts in iterations until the predictions begin becoming true, identifying pictures in a manner comparable to humans.
Distinction between Machine Learning and Computer Vision
| Distinction | Computer Vision | Machine Learning |
| Technologies | Trains computers to recognize visual patterns akin to human vision. | Allows computers to gain insight from inputs of data and respond determined by prior actions, not just visual information. |
| Concern | The main objective is on processing visual data, such as picture categorization and object recognition. | Addresses data kinds other than visual, such as text or audio, with a focus on speech recognition and financial data analytics. |
| Approach | Depends on methods such as Feature Extraction, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), and Image Processing methods. | Algorithms used include Linear Regression, decision trees, Support Vector Machines (SVMs), and Deep learning models. |
| Application | Commonly utilized in medical diagnostics, agriculture, and self-driving vehicles. | Used for speech recognition, financial data analysis, traffic data investigation, email evaluation, and financial technology applications. |
Computer Vision Examples
Many organizations lack the resources required to establish computer vision laboratories and develop deep learning models and neural networks, which can be difficult to go through enormous amounts of visual data. IBM provides computer vision software development tools that supply pre-built learning models from the cloud, reducing requirements on computer resources. Users can access these features via an application programming interface (API) and utilize them to create computer vision applications. IBM also announced IBM Maximo® Visual Inspection, a computer vision platform that enables subject matter experts to mark, train, and implement deep learning vision models without having coding or deep learning knowledge. Here are the some application features:
- Image classification: It forecasts and reliably detects image classification, which helps with tasks like photograph categorization and item identification in a scene.
- Item detection: By identifying and distinguishing item representations inside photos or videos, automated systems may recognize and find individual things in complicated visual situations.
- Object tracking: Once an item is recognized, object tracking methods guarantee that it is continuously monitored, allowing computers to follow its motions and shifts in position continuously.
- Content-based image retrieving: Using computer vision techniques, the app allows the searching, investigating, and retrieval of pictures from large data collections, expediting the process of obtaining important visual information.
Digital asset management systems use these activities to increase browse and retrieval precision, increasing organizational efficiency and production.
Conclusion
Computer Vision and Machine Learning are critical in artificial intelligence that focus on improved accuracy and performance in tasks such as picture categorization, object recognition, and separation. Their combination facilitates the development of effective technological methods, applications, and systems for a variety of businesses and industry sectors. Machine learning has increased computer vision tracking and recognition while providing effective approaches for data collection, digital image processing, and data object identification. Despite its large technological scope, machine learning’s more generic methods may be applied to a variety of different disciplines and fields.