Cryptographic Foundations for Blockchain Security
Blockchain technology represents the future of secure communication, with cryptography playing a pivotal role in safeguarding information. Combining hashing and two encryption methods bolsters blockchain security. This decentralized network hinges on two core elements: blocks, which are data entries, and chains, which serve as public databases. Cryptography forms the crucial link binding these components, establishing the foundation of a blockchain. Over time, this evolving database accumulates records through a series of interconnected blocks, demonstrating the dynamic nature of blockchain technology.
Importance of cryptography in blockchain
Before exploring the principles of blockchain cryptography, it’s crucial to understand the significance of security in blockchain technology. Blockchain is a decentralized ledger database characterized by security, consistency, traceability, reliability, and decentralization. It eliminates the need for traditional node maintenance methods and has developed a novel approach to maintaining core nodes. As a result, security is an essential feature in adding value and fostering trust within the blockchain network.
The decentralized nature of blockchain, with its distributed ledger maintained across multiple nodes, reduces the risk of a single point of failure. However, this decentralized nature also introduces new security challenges. Cryptography plays a critical role in addressing these challenges and ensuring the integrity and security of the blockchain network.
Cryptography in Blockchain
The term “cryptography” originates from the ancient Greek words “kryptos,” meaning “hidden,” and “graphein,” meaning “to write.” It encompasses a set of techniques and methodologies for secure communication and data protection, ensuring that information remains confidential and inaccessible to unauthorized parties.
Cryptography is a vital technique for securing data and transactions in the blockchain. In a blockchain network, the core concepts of cryptography and hashing play a pivotal role. Cryptography encrypts communications within a peer-to-peer (P2P) network, while hashing safeguards data within blocks and establishes the connections between them in the blockchain.
Cryptography’s primary objective is to enhance security for participants, transactions, and the prevention of double-spending. It serves as a protective layer for various transactions on the blockchain, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access, read, and process transaction data, thereby upholding the network’s integrity and trustworthiness.
What are the types of cryptography in Blockchain?
There are two primary types of cryptography:
- Symmetric-key cryptography
- Asymmetric-key cryptograph
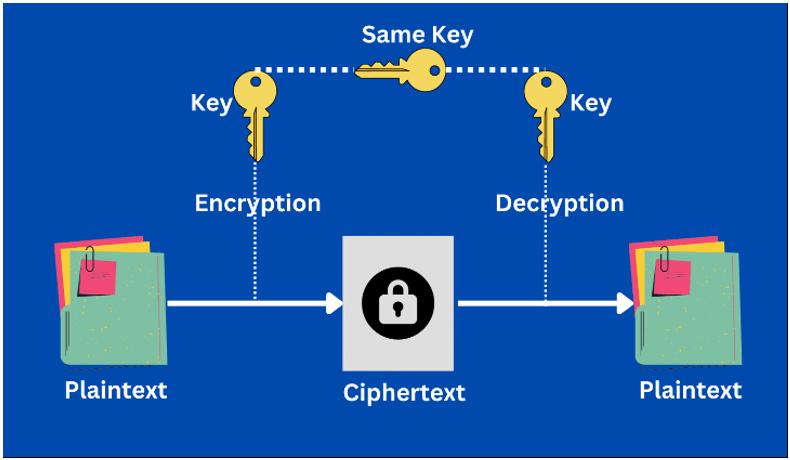
- Symmetric-key cryptography, often referred to as secret-key cryptography, relies on a single shared secret key for both encrypting and decrypting data. This means that the identical key is used to scramble (encrypt) and unscramble (decrypt) the message. While symmetric-key cryptography is cost-effective and computationally efficient, making it suitable for high-volume data encryption, it poses challenges in key management and distribution. The secret key must be kept confidential and shared exclusively with authorized individuals, which can be a more complex process.
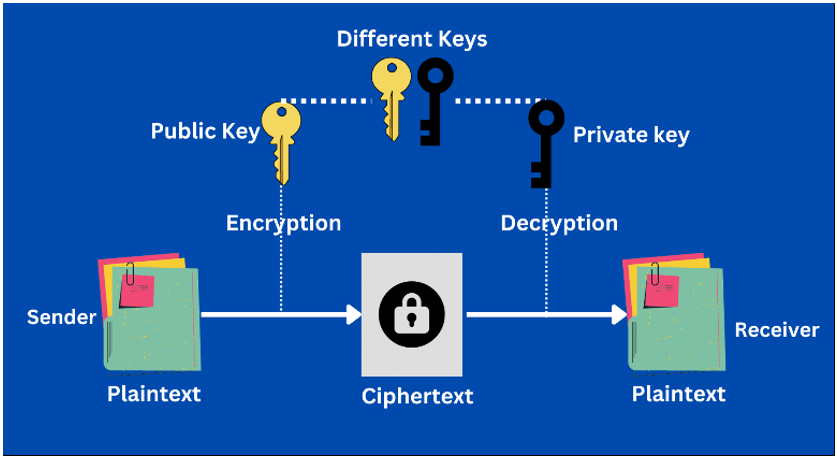
- Asymmetric-key cryptography, often known as public-key cryptography, relies on a pair of mathematically linked keys: a public key and a private key. The public key is freely accessible and can be shared with anyone, while the private key is kept confidential and known only to the owner. In this system, data is encrypted using the public key and decrypted using the private key. Asymmetric-key cryptography is particularly advantageous for secure communication and digital signatures because it eliminates the need for a secure key exchange process, offering a more secure way to protect data and verify identities.
Blockchain technology employs both symmetric-key and asymmetric-key encryption to safeguard the security, integrity, and privacy of transactions and data. Asymmetric-key cryptography implements a pair of mathematically linked keys to secure communication and facilitate digital signatures, while symmetric-key cryptography efficiently encrypts and decrypts large amounts of data using a shared secret key. Additionally, blockchain employs various cryptographic techniques, such as hashing algorithms, digital signatures, and zero-knowledge proofs. These techniques collectively establish a robust foundation for the technology. Such strategies ensure that blockchain transactions are tamper-proof, identities are authenticated, and data is protected from unauthorized access, fostering a reliable and trustworthy platform.
What is the use of Cryptographic Hashing in the Blockchain?
Hashing is a crucial component that enhances blockchain security and immutability. Cryptographic hashing involves transforming data on the blockchain into unreadable, unalterable, and highly secure text. This encryption technique doesn’t rely on keys but uses a cipher to generate a fixed-length hash value from the original data. Any input information can be converted into a unique string of text through hashing, and the resulting hash has a consistent length, regardless of the input’s length. Once the hashing process is complete, it’s irreversible. Even a minor change in the input data results in a completely different hash, making it easy to detect and respond to potential threats, thereby strengthening security in the blockchain.
Hash functions grant each participant a singular perspective of the blockchain, with SHA-256 being a commonly used hashing algorithm in blockchains. This robust combination of cryptographic techniques ensures data security and integrity within blockchain technology.
What are the advantages of cryptography in blockchain?
Security and Privacy
Cryptography ensures the confidentiality and integrity of data on the blockchain. Transactions are encrypted, making it extremely difficult for unauthorized parties to access or alter the information. It allows for the secure sharing of information without revealing sensitive details. Users can transact privately while still benefiting from a transparent and immutable ledger.
Data Integrity
Cryptographic hashing ensures that once data is added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered without detection. This guarantees the integrity of the ledger, making it highly resistant to fraud and tampering.
Conclusion
Cryptography is an essential component of blockchain technology, providing the underlying security, integrity, and anonymity that make blockchain. It would be subject to manipulation, fraud, and illegal access if it did not have strong cryptographic foundations, limiting its general use and success. As blockchain technology evolves, cryptography will be at the forefront of ensuring its security and integrity, allowing it to disrupt numerous sectors and redefine how we communicate and trade in a digital world.