HOW IS MACHINE LEARNING EMBEDDED WITH WIRELESS NETWORKS?
Our society is undergoing a digital revolution, with a dramatic increase in the number of Internet users and linked technologies. In real-time situations, future-oriented wireless connections should enable ultra-reliability, low-latency connectivity and autonomously operate Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Wireless network applications such as real-time traffic statistics, sensor readings from self-driving cars, and media broadcasting suggestions create massive amounts of information that must be received and analyzed in real time. These connectivity’s needs and core cognition can only be met by incorporating machine learning techniques into wireless infrastructure and end-user devices.
A wireless connection allows devices to remain linked without having wires, enabling them to travel without the need for a router. When linked to a location, connections enhance Wi-Fi signals, permitting devices to connect to an organization’s wireless infrastructure.

Machine learning techniques have recently attracted a lot of attention in the field of wireless communication and network design. Machine learning-driven models and techniques can help with wireless network evaluation and the administration of resources, plus handling the increasing volume of communication and computation for emerging networking applications. Nonetheless, the use of machine learning algorithms in heterogeneous wireless systems is still being debated. More efforts are required to bridge the distance between ML and wireless networking technologies.
Wireless networks are being used extensively and established in manufacturing, engineering, weather tracking, transportation, and other fields to collect information and enhance the accuracy of making choices, but challenges such as huge amounts of data, incomplete and inconsistent data sets, and noise information avoid them from recognizing their true value and utilizing their maximum potential. In wireless network programs, machine learning and deep learning approaches have been employed as strong tools for feature detection/extraction and trend estimation/forecasting.
Why wireless networks?
The sole distinction between wireless and wired networks is that wired networks employ connections to connect devices, such as laptops or desktop machines, to the Internet or another network. A wired network has various disadvantages over a network that is wireless. The biggest disadvantage is that a router is connected to your PC. The most common wired networks make use of cables that connect to an Ethernet port on the network router and another end to the machine or additional system.
Potential Wireless network uses
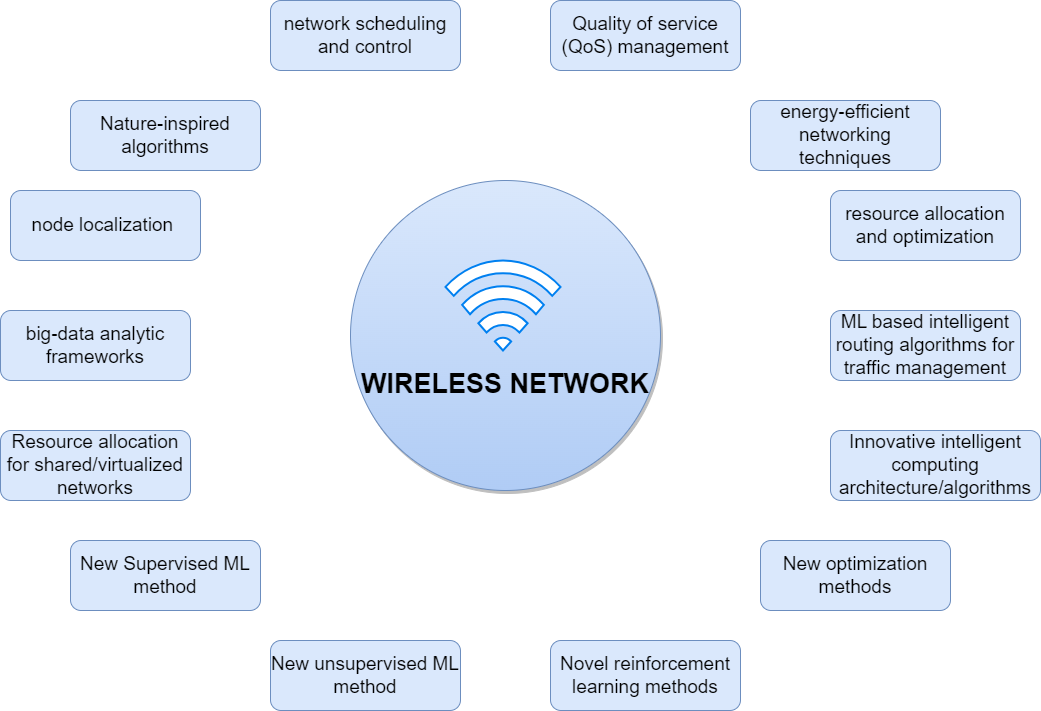
What are the challenges in Wireless Network?
The purpose of special Issue is to investigate recent advances in ML ideas in order to tackle real difficulties in wireless networks which will bring collectively researchers and academics to display novel network modeling and architecture, networking uses, safety and confidentiality, handling resources, distributing load, and many obstacles associated with the design of upcoming wireless networks using machine learning.
ML has the ability to transform wireless networks, but it also introduces new obstacles. Data collection takes time and money, particularly for noisy and inadequate wireless connections. Complexity of models is often an issue, particularly if processing power and energy resources are limited. Machine learning techniques can be affected by disturbance and distortion. For wireless networks that require minimal latency, immediate processing is problematic. Machine learning techniques that analyze private information raise privacy and security problems. Generalization is another issue since they may not generalize effectively to new information, which can be difficult in wireless networks with conditions that are constantly shifting. To tackle these issues, novel solutions and interdisciplinary collaboration among specialists in wireless networking, machine learning, and data analytics will be required.